links: [[2023-07-03-Week]]
要点
Rotary Positional Encoding,通过旋转来去掉绝对位置信息保持相对位置信息的位置编码技术
自注意力的点积不保留绝对位置信息,而保留相对位置信息
通过将 token embedding 表示为复数以实现旋转的位置编码
传统 Positional Encoding
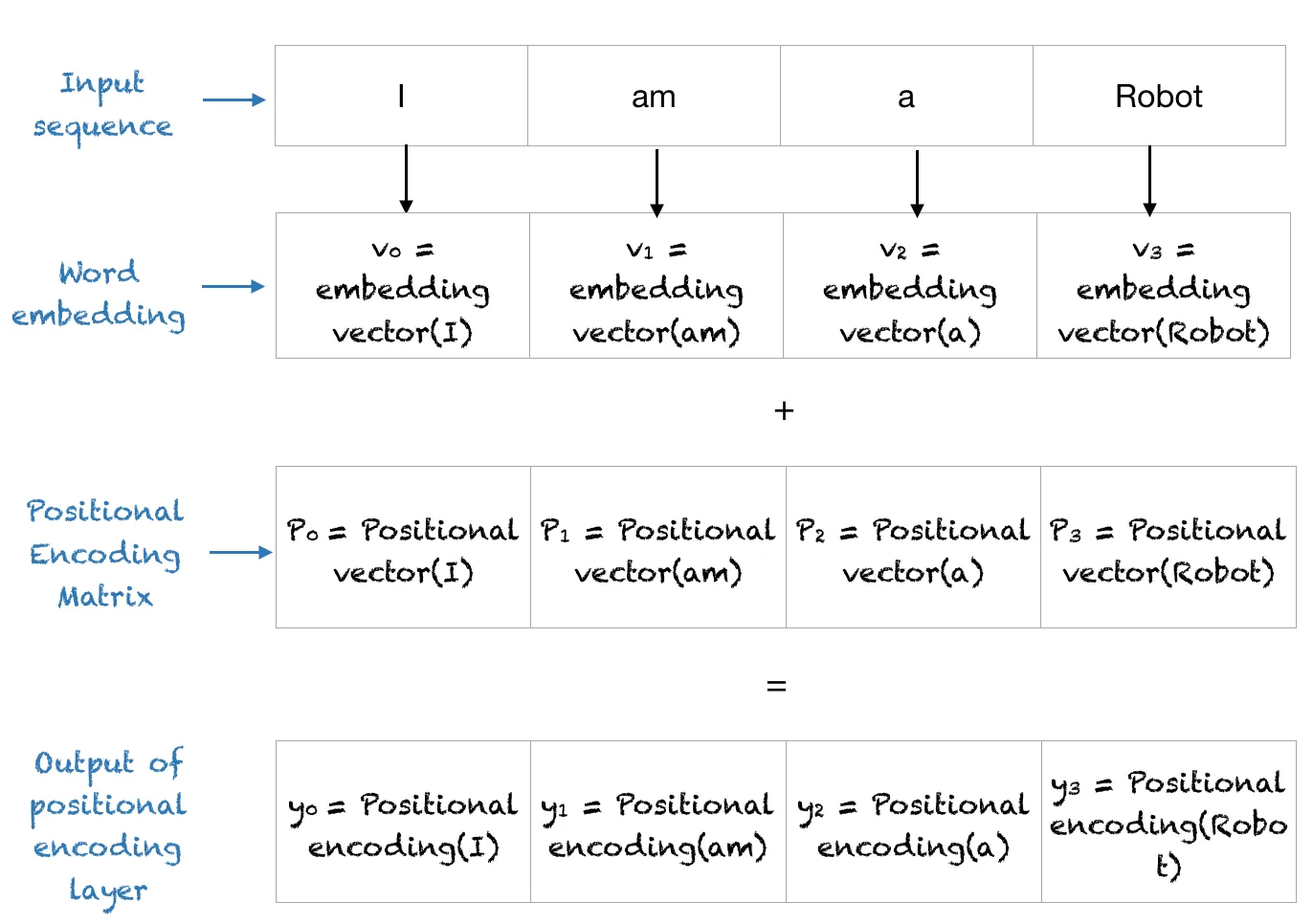
主要包括 Fixed 或 Learned 的 postitional encoding matrix
比如 Fixed:
$$ PE(pos, 2i) = sin(\frac{pos}{10000^{\frac{2i}{d}}}) $$
$$ PE(pos, 2i + 1) = cos(\frac{pos}{10000^{\frac{2i}{d}}})$$
其中,pos 是 word 对应于 sequence 中的位置 idx,i 则是输出 embeddings 序列中的位置(因为输入一个 word 输出是一串 embedding),d 是总 embedding 维数,10000 可以看成基波频率
RoPE 实现
可以看到传统的位置编码是绝对位置编码,实现较为简单,虽然可能推导出具有一定的相对位置编码能力,但还有所不足,为此需要做一些改进。具体原理演进可以参考资料 2-4。总之,RoPE 可以通过绝对位置编码的方式实现相对位置编码,兼得简单与相对编码的好处,而且还能够通过扩展基波频率来无痛加大 context 大小
在代码中表示为:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| base = 10000 # 基波频率
max_position_embeddings = 2048 # 2k context
dim = 512 # 输入维度,也就是 2i 范围
t = torch.arange(max_position_embeddings)
inv_freq = 1.0 / (base ** (torch.arange(0, dim, 2).float() / dim))
freqs = torch.einsum("i,j->ij", t, inv_freq) # torch.outer
# freqs_cis = torch.polar(torch.ones_like(freqs), freqs)
emb = torch.cat((freqs, freqs), dim=-1)
sin_cached = emb.sin()
cos_cached = emb.cos()
|
应用时似乎是乘法的方式,看作是复平面上的旋转操作(和上面的代码不同的实现):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| # 对 attention 的 q k 做旋转
xq_ = torch.view_as_complex(xq_)
xk_ = torch.view_as_complex(xk_)
# xq_out.shape = [batch_size, seq_len, dim]
xq_out = torch.view_as_real(xq_ * freqs_cis).flatten(2)
xk_out = torch.view_as_real(xk_ * freqs_cis).flatten(2)
return xq_out.type_as(xq), xk_out.type_as(xk)
|
扩展 context 的方式包括频率分量上的扩展(次优)
1
2
3
| extend_scale = 4 # max_position_embeddings = 8192
scale = 1 / extend_scale
t *= scale
|
以及基波频率的扩展(NTK-Aware Scaled)
1
2
| extend_scale = 8 # max_position_embeddings = 16384
base = base * extend_scale ** (dim / (dim-2))
|
参考资料
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/642884818
- https://kexue.fm/archives/8130
- https://kexue.fm/archives/8265
- https://kexue.fm/archives/9675
- https://blog.eleuther.ai/rotary-embeddings/
